
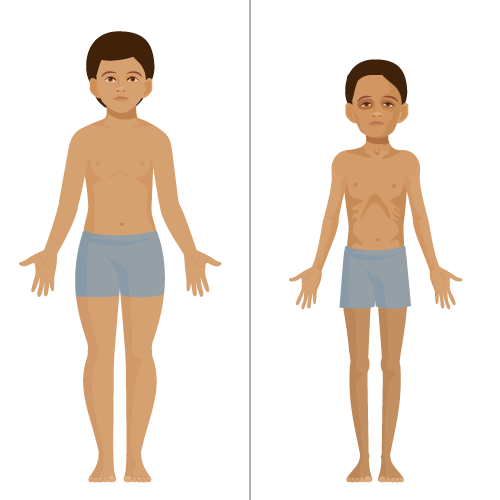

Malnutrition: A Silent Killer We Are Ignoring Malnutrition is one of the most dangerous yet least understood public health problems in the world. It does not always look dramatic. It often hides behind normal faces, average households, and daily meals that seem “sufficient” but are nutritionally poor. Because it grows slowly and silently, many people fail to recognize it until serious damage is already done. That is why malnutrition is rightly called a silent killer.
Contrary to common belief, malnutrition is not only about starvation. A person can eat three times a day and still be malnourished. When the body does not receive the right balance of nutrients — proteins, vitamins, minerals, healthy fats, and calories — it begins to weaken from within. Immunity drops, organs function poorly, growth slows, and disease risk increases. This affects children, adults, and the elderly — especially in low-income and nutritionally unaware communities.
This article explains what malnutrition really is, why it remains hidden, its causes, warning signs, long-term effects, and the urgent actions needed to prevent it.
What Is Malnutrition — The Real Meaning
Malnutrition is a condition that occurs when the body gets too little, too much, or the wrong balance of nutrients. It has three major forms:
1️⃣ Undernutrition
- Too few calories
- Too little protein
- Vitamin and mineral deficiencies
- Low body weight
- Stunted growth in children
2️⃣ Micronutrient Deficiency
- Lack of iron, vitamin A, iodine, zinc, B12, etc.
- Often invisible at first
- Causes long-term damage
3️⃣ Overnutrition (Hidden Malnutrition)
- Excess calories but poor nutrients
- Junk food diets
- Obesity with deficiencies
- “Overfed but undernourished”
This third category is rising rapidly in urban populations — people eat enough calories but lack real nutrition.
Why Malnutrition Is Called a Silent Killer
Malnutrition rarely kills suddenly. Instead, it weakens the body gradually:
- Immunity becomes weak
- Infections become frequent
- Recovery becomes slow
- Organs become stressed
- Growth and cognition decline
Deaths often occur due to infections, childbirth complications, or chronic illness — but the hidden root is nutritional weakness.
According to global nutrition reports from organizations like World Health Organization and UNICEF, millions of children worldwide suffer growth and immunity damage due to poor nutrition — even where food is available.
Major Causes of Malnutrition
Poor Diet Quality
The biggest cause is not always lack of food — but lack of nutrient diversity:
- Refined grains only
- Low protein intake
- No fruits or vegetables
- No healthy fats
- Processed foods replacing real food
Poverty and Food Insecurity
Low income limits access to:
- Protein foods
- Fresh produce
- Dairy
- Nuts and seeds
Families fill stomachs with cheap calories instead of nutrition.
Lack of Nutrition Education
Many households do not know:
- What nutrients are needed
- Child feeding practices
- Balanced plate concept
- Importance of protein
Knowledge gap = nutrition gap.
Disease and Absorption Problems
Even with food intake, diseases can cause malnutrition:
- Chronic diarrhea
- Gut infections
- Worm infestations
- Malabsorption disorders
Nutrients are eaten but not absorbed.
Maternal Malnutrition
If a mother is malnourished:
- Baby is born low weight
- Brain development suffers
- Growth risk increases
Malnutrition can begin before birth.
Warning Signs of Malnutrition
Malnutrition signs are often ignored because they develop slowly.
In Children
- Slow growth
- Thin arms and legs
- Swollen belly (protein deficiency)
- Frequent illness
- Low attention span
- Delayed milestones
In Adults
- Constant fatigue
- Hair fall
- Pale skin
- Frequent infections
- Muscle loss
- Poor wound healing
In Elderly
- Weakness
- Appetite loss
- Weight loss
- Bone fragility
Effects of Malnutrition on the Body
Immune System Damage
Nutrient deficiency weakens immune cells. Minor infections become serious. Recovery takes longer.
Brain Development Impact
In children, poor nutrition affects:
- IQ
- Memory
- Learning ability
- Behavior control
Some damage is irreversible if it occurs early.
Growth Failure
Chronic malnutrition leads to:
- Stunting
- Low height for age
- Reduced muscle mass
Increased Disease Risk
Malnutrition increases risk of:
- Tuberculosis
- Pneumonia
- Anemia
- Pregnancy complications
- Surgical complications
Productivity Loss
Adults with poor nutrition:
- Have low work capacity
- Tire easily
- Earn less
- Remain trapped in poverty cycle
Hidden Urban Malnutrition
Modern cities show a new pattern:
People eat:
- Fast food
- Sugary drinks
- Refined snacks
But lack:
- Fiber
- Micronutrients
- Quality protein
Result:
Obesity + deficiency together
This is called hidden hunger.
Malnutrition in Children — The Most Dangerous Form
Children suffer the most severe long-term consequences:
- Brain development window is limited
- Early deficiency causes permanent loss
- School performance declines
- Adult earning capacity drops
Child malnutrition is not just a health issue — it is a national development issue.
The Role of Protein Deficiency
Protein is often the missing nutrient in low-income diets.
Protein deficiency leads to:
- Muscle wasting
- Edema
- Weak immunity
- Slow recovery
- Growth failure
Affordable protein sources include:
- Lentils
- Chickpeas
- Groundnuts
- Eggs
- Milk
- Soy
How to Prevent Malnutrition
Balanced Plate Rule
Each meal should include:
- Protein source
- Whole grains
- Vegetables
- Healthy fats
- Fruit
Improve Child Feeding
- Exclusive breastfeeding first 6 months
- Add protein foods early
- Avoid only-starch diets
Use Local Nutritious Foods
Low-cost nutrition foods:
- Millets
- Pulses
- Seasonal vegetables
- Groundnuts
- Curd
Deworming and Gut Health
Treat worm infections and chronic diarrhea — or nutrients won’t be absorbed.
Maternal Nutrition Programs
Healthy mothers → healthy babies.
School Nutrition Programs
Midday meal quality matters — not just calories.
Community and Policy Responsibility
Malnutrition cannot be solved by individuals alone. It requires:
- Public nutrition education
- Food fortification
- School feeding quality
- Maternal support programs
- Clean water and sanitation
- Primary health screening
Governments, NGOs, schools, and families must work together.
The Cost of Ignoring Malnutrition
Ignoring malnutrition leads to:
- Higher healthcare costs
- Lower workforce productivity
- Higher child mortality
- Poor educational outcomes
- Intergenerational poverty
Nutrition is not an expense — it is an investment.
Final Message
Malnutrition is dangerous not because it is rare — but because it is common and unnoticed. It weakens bodies, limits minds, and reduces human potential silently. A full stomach does not always mean a nourished body. True nutrition requires balance, diversity, and awareness.
If families, schools, and communities focus on nutrient quality — not just food quantity — this silent killer can be stopped. Early action, local foods, protein inclusion, and nutrition education are the most powerful weapons we have.
Global Malnutrition Crisis: Key Facts
- India ranks 111th (out of 121) in the 2023 Global Hunger Index—worse than Nepal, Pakistan, and Bangladesh.
- UNICEF reports 1 in 3 children globally suffer from stunting.
- WHO highlights:
- 45 million children are wasted.
- 148 million are stunted.
Malnutrition in India: Shocking Statistics
NFHS-5 (2019-21) Data:
- 35% of under-5 children are stunted (low height-for-age).
- 32% are underweight.
- 19% suffer from wasting (severe weight loss).
State-wise Breakdown
| State | Stunting (%) | Underweight (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Bihar | 42.9 | 41.0 |
| Uttar Pradesh | 39.7 | 32.1 |
| Karnataka | 35.4 | 32.9 |
| Kerala | 23.4 | 19.7 |
Alarming Fact: 51.8% of women in Karnataka are anaemic—a key indicator of malnutrition.
Root Causes of Malnutrition
- Poverty & Food Insecurity – Inability to afford diverse, nutrient-rich foods.
- Poor Maternal Health – Malnourished mothers give birth to underweight babies.
- Lack of Awareness – Misconceptions about balanced diets.
- Sanitation Issues – Repeated infections worsen nutrient absorption.
- Limited Diet Diversity – Over-reliance on rice/wheat, lack of proteins & vitamins.
Consequences of Malnutrition
- Children: Impaired brain development, lower IQ, higher school dropout rates.
- Adults: Reduced work productivity, higher disease susceptibility.
- Economy: India loses 4% of GDP annually due to malnutrition (World Bank).
India’s Fight Against Malnutrition
- POSHAN Abhiyaan – Aims to reduce stunting by 2025.
- Mid-Day Meal Scheme – Provides nutritious meals to schoolchildren.
- ICDS (Anganwadi Services) – Targets pregnant women & children under 6.
- Anaemia Mukt Bharat – Focuses on iron & folic acid supplements.
How You Can Help
✅ Educate – Share nutrition knowledge in your community.
✅ Support – Donate to NGOs like Akshaya Patra, CRY, or local food drives.
✅ Advocate – Push for better policies on food security & healthcare.
Conclusion: A Call to Action
“Are you giving your child what their body really needs?”
Malnutrition isn’t inevitable—it’s solvable. By raising awareness, supporting programs, and demanding policy changes, we can build a healthier, stronger India.
Let’s act today—because no child should grow up hungry.

